UX
of interaction and flow in Virtual Reality.

Overview
The Problem
There are a variety of interaction options in VR for using your hands, which one allows for the best level of user experience when executing tasks.
Goal
Understand and determine the connections between interaction types and flow, presence and immersion.
Approach
Design a series of tasks that are similar but with different controls, physical VR controllers, hand-tracking and actual hands as a control.
Methods & Tools
UX & interaction design research, Ethnography, Usability testing, Interviews, Virtual Reality Development (Unity, HTC Vive, Leapmotion)
Time
6 months (2019)
Background
Virtual Reality is not a new piece of technology and its existence has been around for a couple of decades. The current wave of VR today is attributed to the advancements of technology, making it relatively much cheaper and available to the masses. As such VR development and utilization is still in a very early stage, much is still being discussed and explored.
In this project, the goal was to find out more about the interaction of VR. Specifically what are the affordances and the implications of the different types of interaction and its relation to the user experience (UX) itself. This is a crucial first stage if VR is going to be utilized as a tool in areas such as research, education and training.
Background
Virtual Reality is not a new piece of technology and its existence has been around for a couple of decades. The current wave of VR today is attributed to the advancements of technology, making it relatively much cheaper and available to the masses. As such VR development and utilization are still in a very early stage, much is still being discussed and explored.
In this project, the goal was to find out more about the interaction of VR. Specifically, what are the affordances and the implications of the different types of interaction and its relation to the user experience (UX) itself. This is a crucial first stage if VR is going to be utilized as a tool in areas such as research, education and training.
User Testing
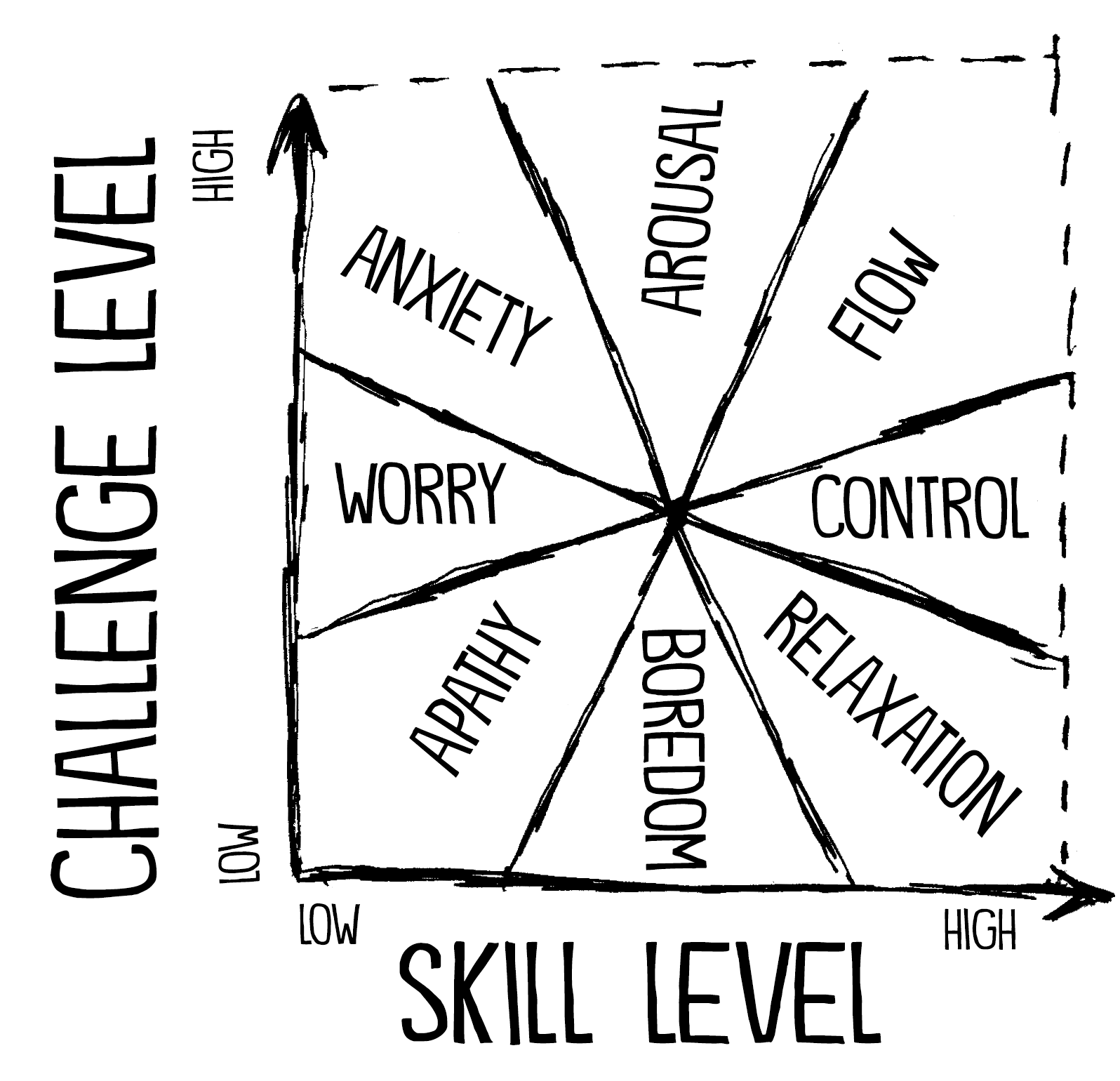
Theory & connection to study
In VR there are 2 important factors that can determine if an experience is successful or not. The first is presence and the second is immersion. A designer and developer can design for immersion; however, presence is something that happens on the end of the user. There are multiple different nuances that can contribute to presence such as the user’s willing suspension of disbelief. In my research, I have discovered some overlapping similarities between characteristics of presence and that of flow, which is from flow theory in psychology. (Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi) An illustration of flow theory can be seen from the diagram.
The test here is to utilize measurements in flow theory to see how it may relate to measuring presence in VR. As such this will give an insight to designers and developments what should be done when creating interaction in VR.
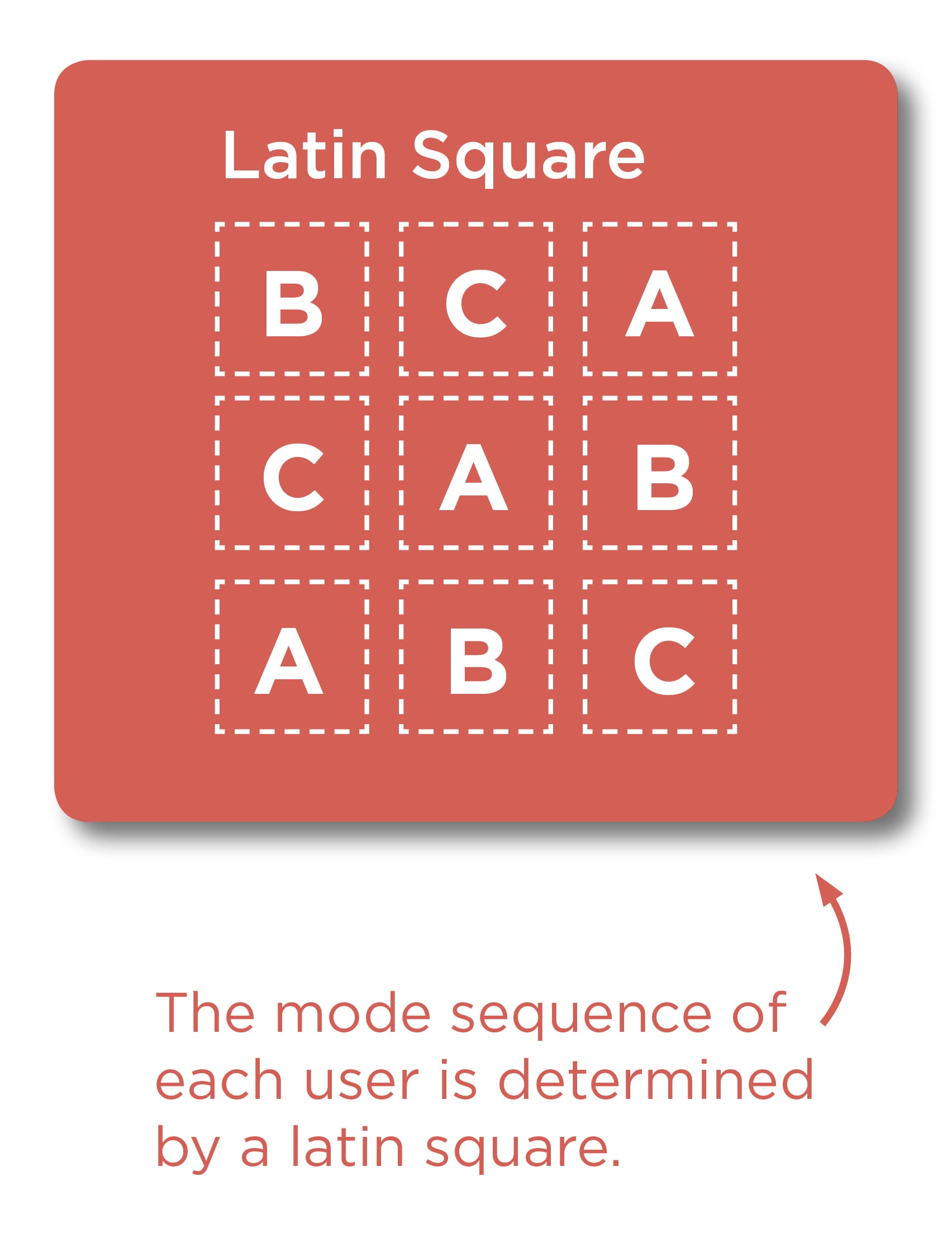
Study Design Plan
There are a total of 3 different modes of interaction that each user going through the test has to complete. In order to maintain proper unbiased data, a Latin square has been adopted to determine the sequence of each participant. This is randomly assigned to a participant in relation to their participant number.

VR Development
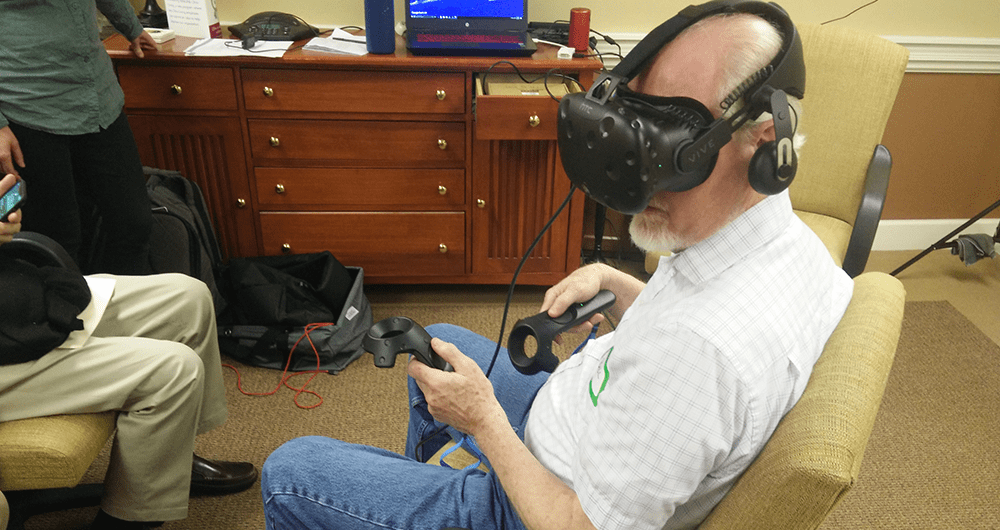
The development of the VR environment went through multiple iterations. In its core, there were two specific interaction systems that needed to be included in the design. The first is the HTC Vive controllers and the second is the leapmotion hand tracking device. Each had a different level of interaction, engagement, control, precision and a learning curve. Here you see a clip of an early test of the hand tracking interaction.
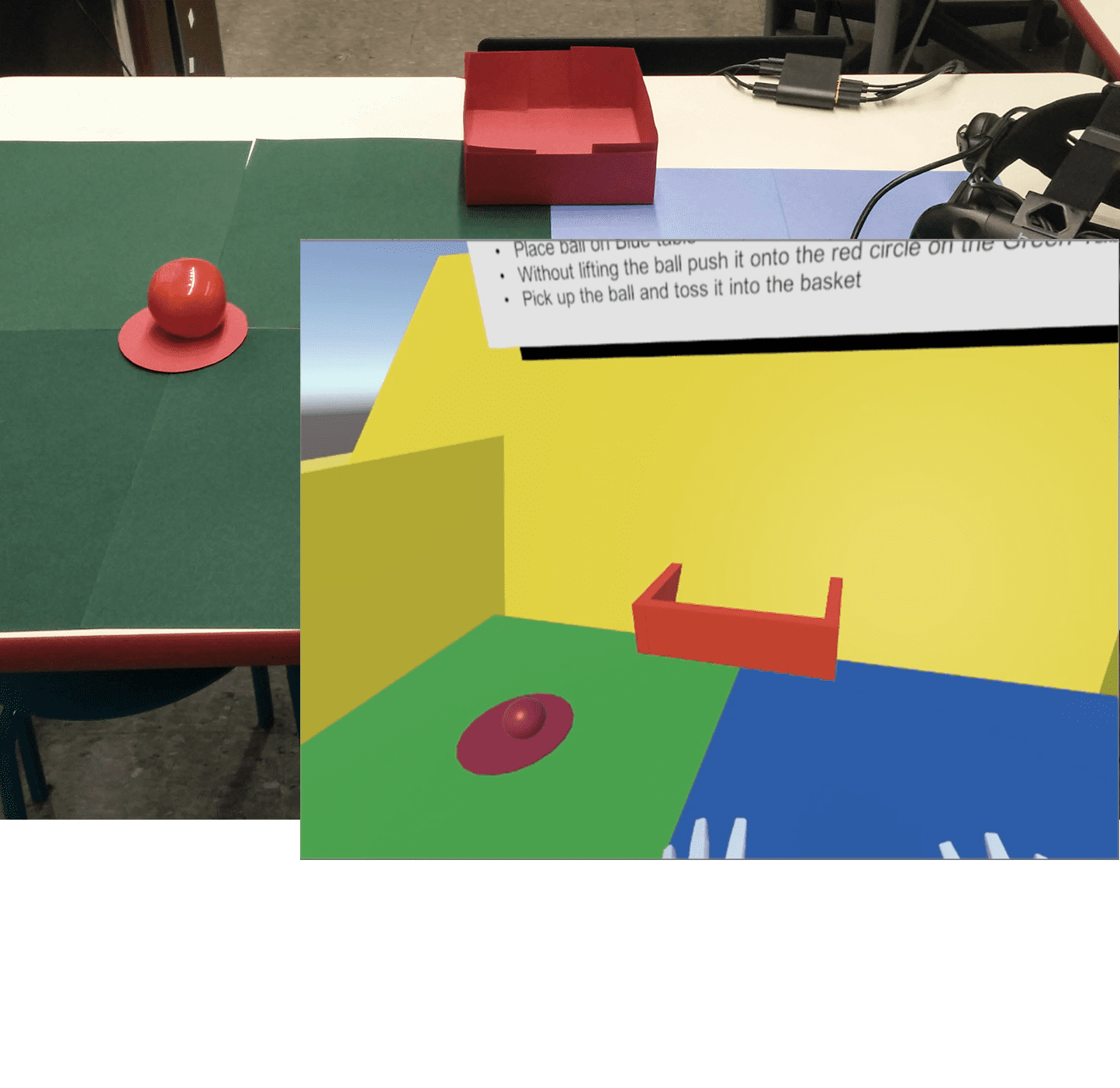
Task & Environment (Physical & VR)
The environment between the physical world and virtual reality was designed to reflect each other. This will enable a fair test and creates a cognitive similarity for participants. The task sequence is as follows:
1 Pick up ball from the green area with primary hand
and transfer to secondary hand
2 Place ball on the blue area
3 Move ball without lifting onto the red dot
4 Pick up and toss the ball into the red box
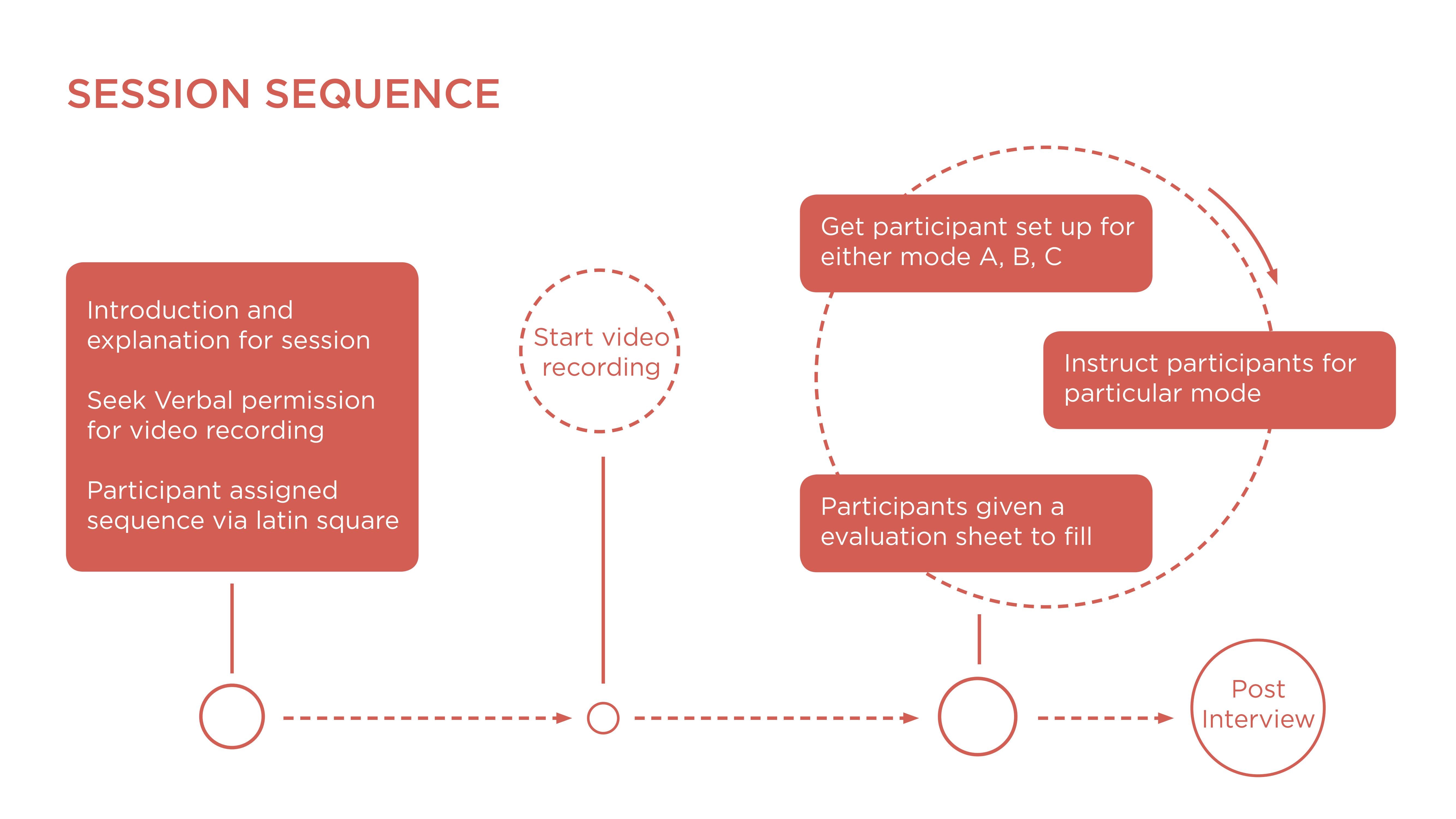
Data capture & Sample

Data captured for analysis included video recording, screen capture, observational notes, and a questionnaire that was designed based on flow and engagement. Here is a clip of one of the participants in the hand-tracking sequence. The sample of participants had no prior VR experience so the interaction was new for them.
Analysis
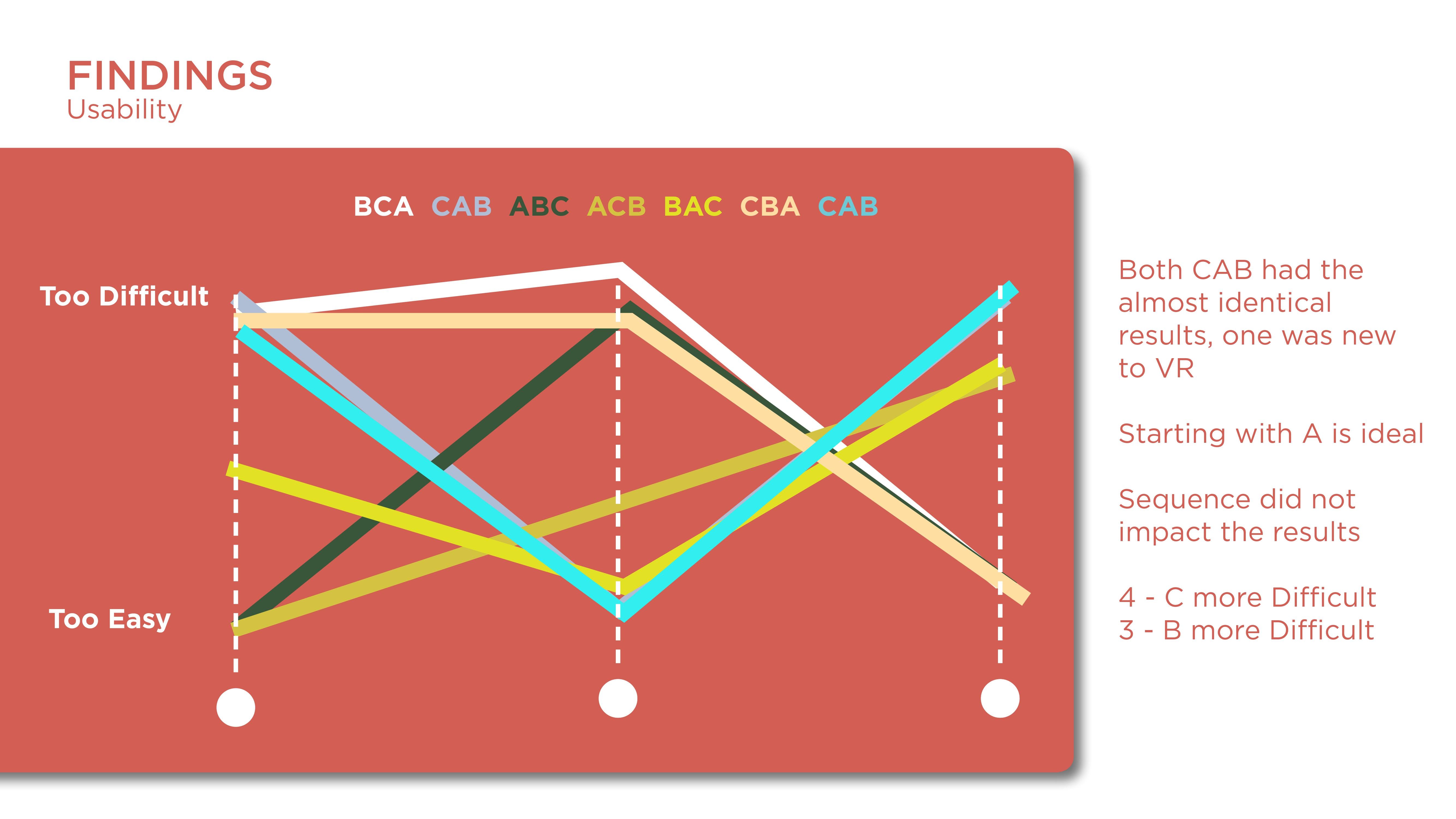
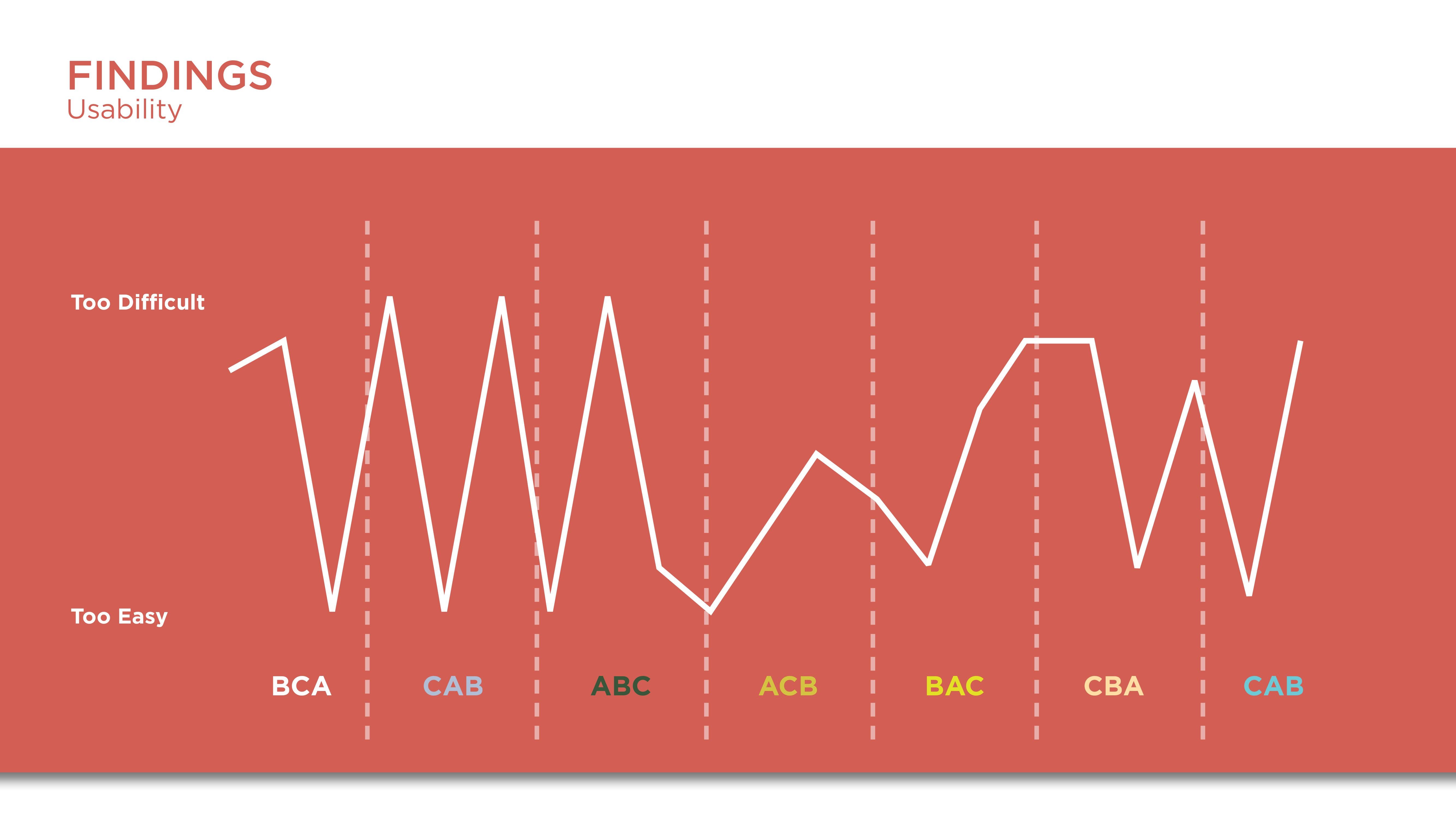
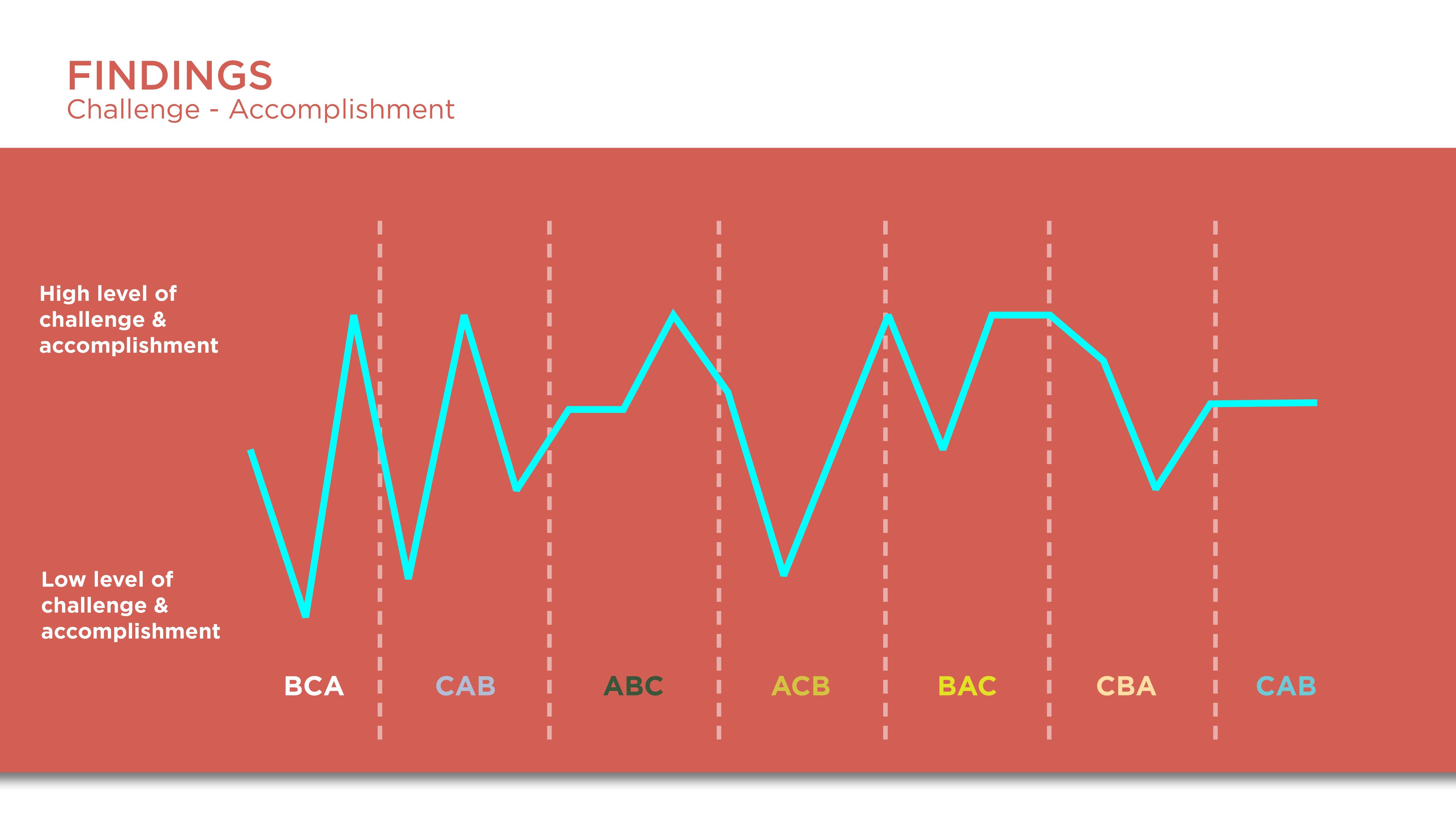
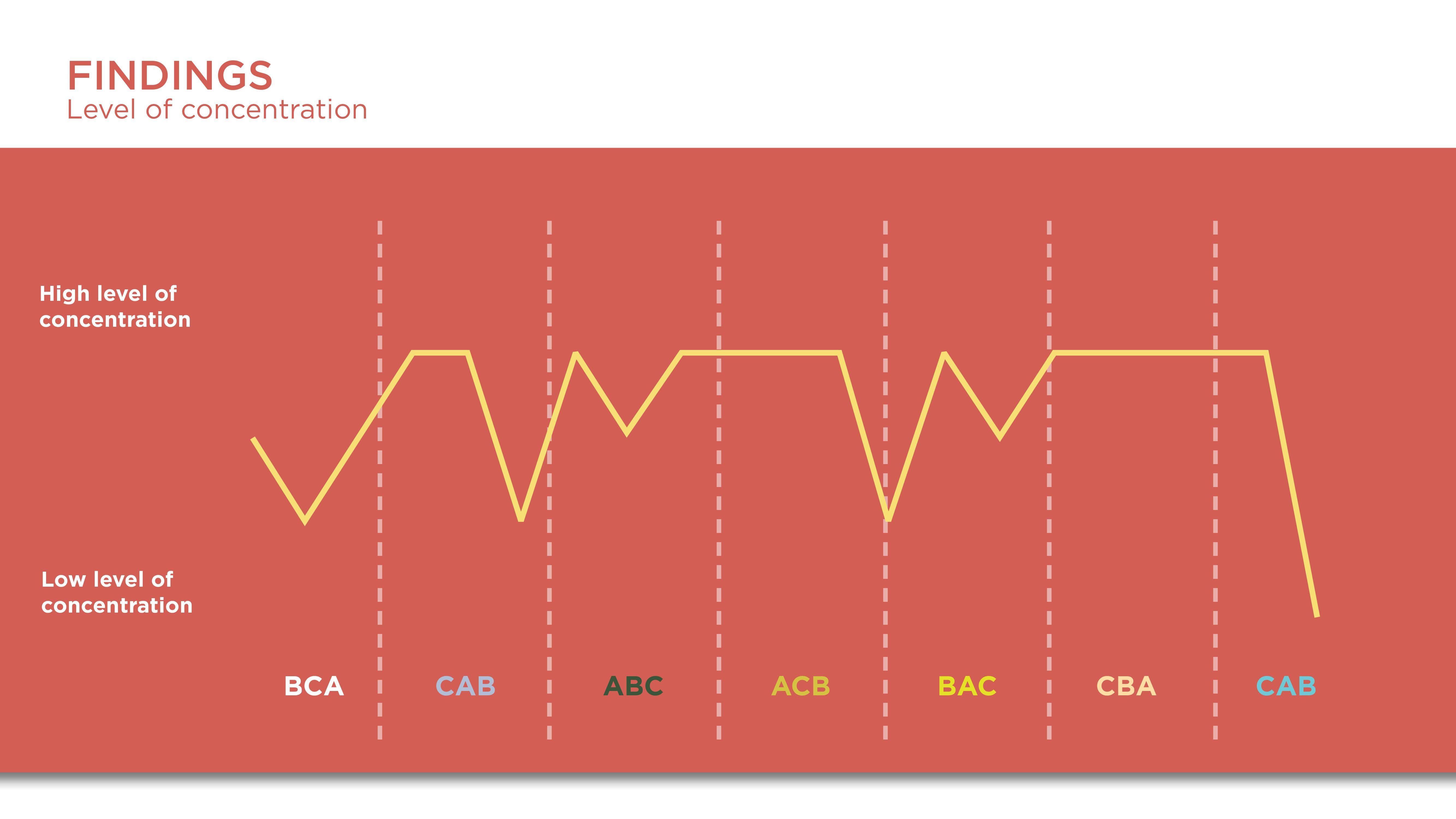
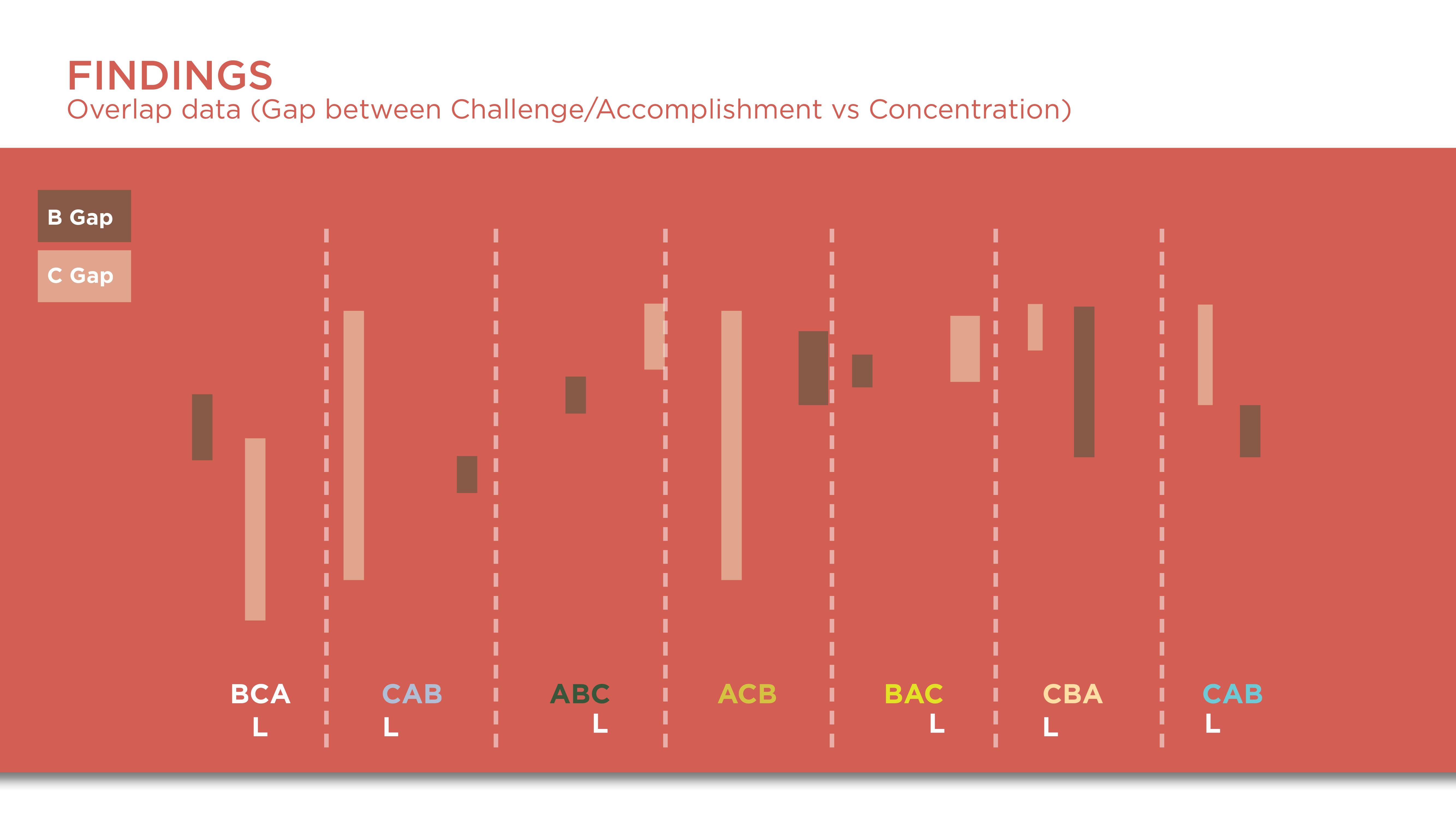
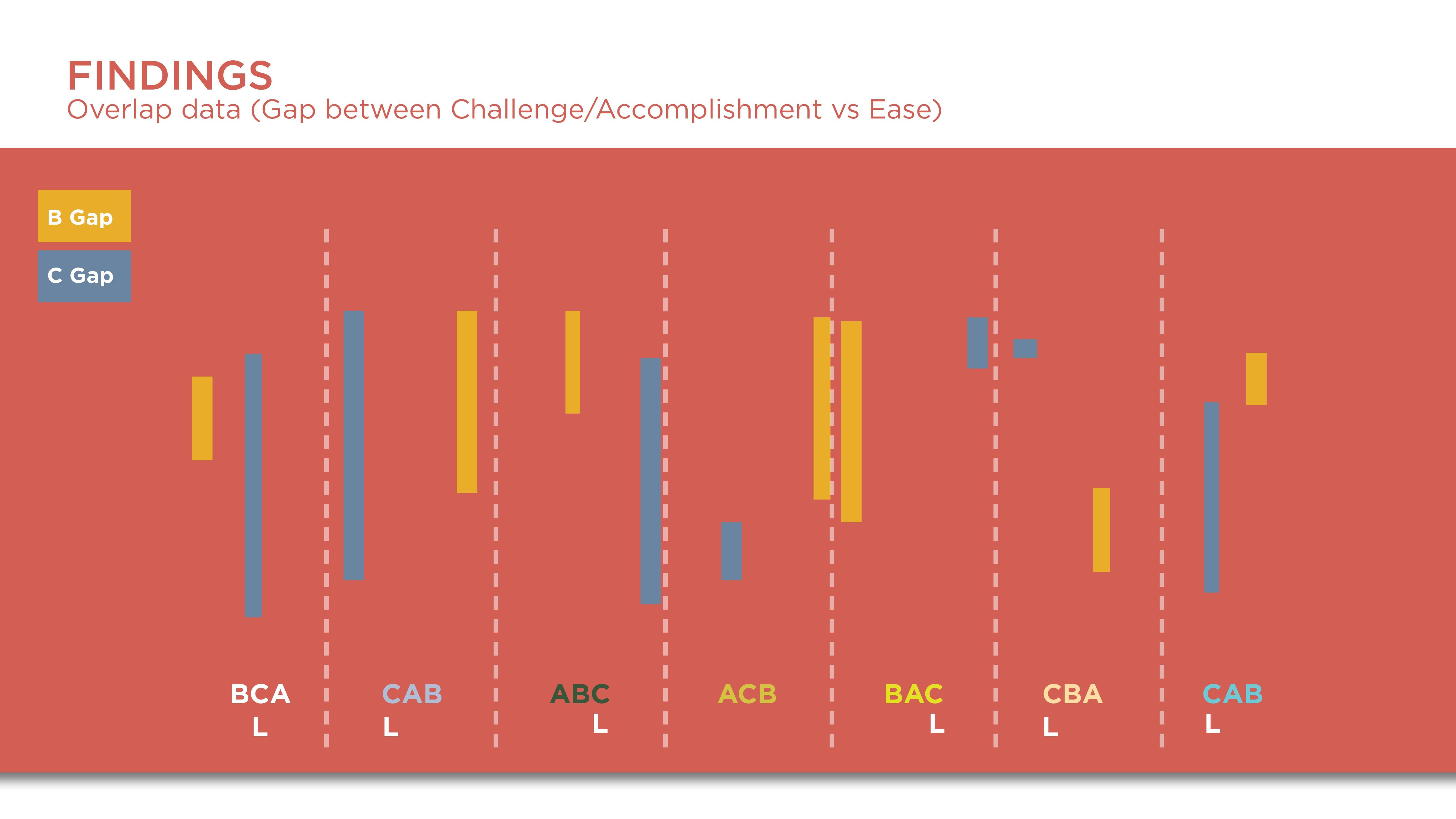
Constant results from the questionnaire showed that participants felt they were in most control in C which was the Vive controllers. It is interesting that the initial perceptions of participants were that the hand tracking was more easy and fun but after going through the task the limitations of the hardware led them to favor the controllers more.
Some of the takeaways from the study is that:
The preference for the Vive controllers is due to more control.
The dislike and break of flow and engagement of participants with hand tracking are due to the uncanny valley.
Though hand-tracking was closer to realistic interaction, the use of controllers as hands became more natural after some time of concentrating on the task. This could be due to cognitive effects such as common coding theory.
This study led to another more specific pilot study on flow which can be downloaded here if you are interested in the findings.
Check out my other projects

PAUSEture A healthier work setupProduct Design & Human Factors

Co-Design of future driving consoleUX Research Methods & VR

PolyStroid Virtual Reality DevelopmentInteraction Design & VR
AR App: 5 Lvls of Autonomous DrivingInteraction Design & AR

Mixed in Reality - What if?Speculative Design

VR Collaborative SandboxVR Make Space

Virtual Reality MuseumVR & Experiential

Ohio Living Wellbeing Online PortalUX research & Co-design

Reducing sleep deprivation and delirium in the ICU (Wexner Medical Center)UX Research Methods, Remote
Phone. SixOneFour 467 ZeroFiveThreeZero
Phone. SixOneFour 467 ZeroFiveThreeZero
Phone. SixOneFour 467 ZeroFiveThreeZero
Phone. SixOneFour 467 ZeroFiveThreeZero
City. Columbus OHIO
City. Columbus OHIO
City. Columbus OHIO
City. Columbus OHIO
M. F. Y. C. | User Experience Research | ImmersiveTechnologies (AR & VR) |
M. F. Y. C. | User Experience Research | ImmersiveTechnologies (AR & VR) |
M. F. Y. C. | User Experience Research
| ImmersiveTechnologies (AR & VR) |
© 2021 mfycdesign
© 2021 mfycdesign
© 2021 mfycdesign




